The Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine combines two essential functions, dispersion and grinding, into a single process. It can serve as both a dispersion machine and a grinding machine, enabling the sequential dispersion and grinding of materials. Compared to conventional equipment for coatings production, which typically involves separate dispersion and grinding machines, the Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine offers several advantages, including simplified processes, ease of operation, high efficiency, convenient cleaning and color changes, minimal residue in containers, cost-effectiveness, and straightforward maintenance. This article primarily discusses the feasibility of achieving integrated dispersion and grinding functions within its structural design.
In the production of coatings, especially for liquid materials with solid particulate aggregates, a dispersion machine is often used to pre-disperse the materials within the container before transferring them to a sand mill for grinding to the desired fineness. However, this production process involves the setup of pipelines, pumps, and the exchange of containers, making it complex and time-consuming. Furthermore, frequent container changes result in material residue, leading to raw material wastage and increased costs. Presently, existing basket-type grinding machines possess some dispersion capabilities, but dispersion and grinding are carried out separately on two different machines. This prevents full automation in production and results in subpar grinding outcomes, particularly for materials with high solid content or viscosity. For such cases, using a dispersion machine for pre-dispersion is essential.
Currently, the utilization of equipment that can both pre-disperse and grind materials in coating production is not widespread. This study aims to compare traditional coating production equipment with the Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine and provide insights into the feasibility of its application.
1. Principle Analysis
1.1 Traditional Coating Production Equipment
In the traditional coating production process, as illustrated in Figure 1, a separate dispersion machine is employed to pre-disperse and mix the slurry materials. After thorough mixing and dispersion, the material is pumped into a sand mill for grinding solid particles to the desired fineness. If the desired fineness is not achieved after grinding, the material is recycled through the sand mill until the required fineness is obtained.
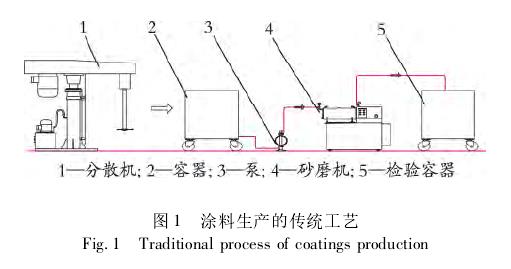
Figure 1 shows that Dispersion Unit 1 disperses the materials within Container 2, and after adequate mixing and dispersion, Container 2 is transported to Sand Mill 4 via Pump 3. Following grinding in Sand Mill 4, the material is stored in Container 5. If the fineness is unsatisfactory, Container 5 is returned to Container 2 for re-grinding. Once the material in Container 5 meets the process requirements, the grinding process is halted. The material in Container 5 becomes a semi-finished coating. This process is straightforward but labor-intensive due to frequent container exchanges, resulting in material wastage.
1.2 Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine
The Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine, as depicted in Figure 2, revolutionizes the traditional coating production process by consolidating dispersion and grinding into a single machine. It offers simplicity of operation, minimal waste, precise quality control, and automation feasibility.
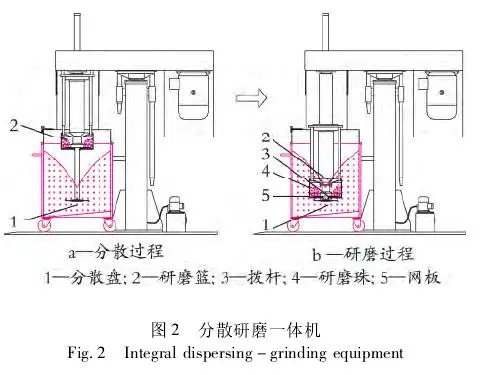
This machine is designed for grinding materials in a liquid phase, including tiny and finely dispersed solid components. The grinding process consists of four steps:
(1) Under the action of the high-speed rotating dispersion disc, larger particle aggregates (powder clumps) are broken down into smaller particle aggregates.
(2) Stabilization of the initial particles, chunks, and aggregates to reconstitute them.
(3) The grinding basket descends to the working position, and the material to be ground is drawn into the grinding basket. The lever arms on the impeller wheel rotate rapidly, moving the grinding beads to refine the material.
(4) Material is discharged from the bottom of the grinding basket through a dense mesh plate.
As shown in Figure 2, during the dispersion process, Dispersion Disc 1 is in the working position while the grinding basket is in the parked position. During this phase, Dispersion Disc 1 efficiently and rapidly performs pre-dispersion. In the grinding process, both the grinding basket and Dispersion Disc 1 are in the working position, and the material to be ground is drawn into the grinding basket. Lever arm 3 rotates at high speed, moving grinding beads 4 to refine the material. Subsequently, the material is expelled from the bottom of the grinding basket through mesh plate 5. The Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine integrates both dispersion and grinding processes into one machine or can be used independently as a dispersion machine. It delivers excellent grinding results, even for materials with high solid content or viscosity. Its advantages include simplicity, reduced processing time, high efficiency, minimal residue, and convenient cleaning and color changes.
2. Structure of the Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine
2.1 Structure
The structure of the Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine, as shown in Figure 3, consists of the following key components:
Base Structure (Hydraulic Lifting Frame 1): The base structure comprises the base, columns, hydraulic lifting cylinders, crossbeam, and other components. All other parts are mounted on this structure.
Dispersion Components (Component 7): This includes key elements such as the drive pulley 15, main spindle 16, dispersion machine frame 17, lower clutch 20, and dispersion disc 25. Inside the dispersion machine frame, a pair of bearings supports the main spindle. When the grinding components are in the parked position, the dispersion components operate to disperse the material.
Grinding Components (Component 8): This includes upper clutch 18, grinding machine frame 19, grinding basket 21, lever arm impeller 22, zirconia beads 23, and mesh plate 24. When the grinding components are in the working position, they perform grinding operations on the material.
Drive System (System 13): This system provides power to either the dispersion or grinding components. It transmits kinetic energy from the main motor to the dispersion components using a pair of pulleys. Depending on the production process requirements, when the two air cylinders of this equipment are actuated, they push downward, causing precise engagement between the upper and lower clutches. This allows the kinetic energy from the main motor to be transferred from the dispersion components to the grinding components.
Electrical Control System (System 14): The control system utilizes a PLC controller and touchscreen interface, ensuring precise control and ease of operation.
2.2 Operational Process
As illustrated in Figure 3, the grinding components are in the parked position (Figure 3-2), ensuring they do not contact the material to be dispersed. During pre-dispersion, the dispersion disc rotates, and its height can be adjusted to ensure optimal processing conditions. Ideal "ring-effect dispersion" is achieved during pre-dispersion. The grinding components remain inactive, allowing the dispersion disc to rapidly and effectively perform pre-dispersion.
As depicted in Figure 3-3, when both air cylinders are actuated, they push the upper clutch 18 and lower clutch 20 into precise engagement, thereby causing the dispersion components to drive the rotation of the grinding components. At this point, the grinding basket 21 is fully immersed in the material to be dispersed. The grinding machine frame 19 causes the lever arm impeller 22 to rotate relative to the grinding basket 21. The lever arm impeller 22 sets the zirconia beads 23 in motion, effectively grinding the material within the grinding basket. A mesh plate 24 is installed at the bottom of the grinding basket. When the dispersion disc 25 rotates at high speed, centrifugal force creates a negative pressure at the center of the dispersion disc, suctioning the finely dispersed and ground material through the mesh plate. Through this fluid process, the material achieves fine dispersion and grinding.
3. Conclusion
The Integrated Dispersion and Grinding Machine combines the strengths of a dispersion machine and a basket-type grinding machine, offering a compact, highly automated, and user-friendly solution with precise control and environmental friendliness. It is well-suited for industrial-scale production. In recent years, its application in the dispersion and grinding of solid particles in a liquid phase, especially in coatings production, has garnered attention and delivered economic and social benefits. We anticipate that its usage will expand beyond the coatings industry to other sectors.

Submit your demand,
we will contact you ASAP.

Sanxin New Materials Co., Ltd. focus on producing and selling ceramic beads and parts such as grinding media, blasting beads, bearing ball, structure part, ceramic wear-resistant liners, Nanoparticles Nano Powder

