I. Introduction
In the era of rapidly evolving transportation and energy sectors, solid-state batteries have emerged as a revolutionary technology with the potential to reshape the future of electric vehicles and energy storage. As the global push for sustainable mobility intensifies, China, being a major player in the battery industry, is witnessing a fierce race among companies vying to establish dominance in the solid-state battery market. This article delves deep into the current state, challenges, and future prospects of China's solid-state battery industry, with a particular focus on its leading enterprises.
II. Advantages and Development Trends of Solid-State Batteries
A. Advantages of Solid-State Batteries
High Energy Density
Solid-state batteries offer significantly higher energy density compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This means they can store more energy in the same volume or weight, enabling electric vehicles to achieve longer driving ranges. For instance, a solid-state battery-powered electric vehicle could potentially travel several hundred more kilometers on a single charge than its lithium-ion battery counterpart. This is a crucial factor for consumers who are concerned about range anxiety and is one of the main drivers for the development of solid-state batteries.
Enhanced Safety
The use of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries provides a major safety advantage. Unlike liquid electrolytes in conventional batteries, solid electrolytes are non-flammable and less prone to leakage. This reduces the risk of battery fires and explosions, making solid-state batteries a safer option for electric vehicles. In addition, solid-state batteries are more stable under extreme conditions such as high temperatures and mechanical stress, further enhancing their safety profile.
Long Lifespan
Solid-state batteries have the potential for a longer lifespan due to several factors. The solid electrolyte is less likely to degrade over time compared to liquid electrolytes, reducing the loss of battery capacity. Moreover, the absence of liquid electrolytes also minimizes the occurrence of side reactions that can damage the battery. This longer lifespan not only benefits consumers by reducing the need for frequent battery replacements but also has positive implications for the overall sustainability of electric vehicles.
B. Development Trends of Solid-State Batteries
Technological Advancements
As research and development efforts continue, significant technological advancements are expected in the field of solid-state batteries. This includes the development of new materials for solid electrolytes, electrodes, and separators that can improve the performance and stability of the batteries. For example, researchers are exploring the use of novel solid electrolytes with higher ionic conductivity to enhance the charging and discharging rates of solid-state batteries. Additionally, advancements in electrode materials could lead to increased energy storage capacity and better cycling performance.
Cost Reduction
Although solid-state batteries currently have a higher cost compared to traditional batteries, efforts are underway to reduce their cost. This can be achieved through various means such as improving manufacturing processes, scaling up production, and finding cheaper materials. As the technology matures and production volumes increase, the cost of solid-state batteries is expected to come down, making them more competitive with traditional batteries.
Expansion of Application Areas
Beyond electric vehicles, solid-state batteries have the potential to be used in a wide range of applications. For instance, they could be used in energy storage systems for renewable energy integration, portable electronics, and aerospace applications. The versatility of solid-state batteries could open up new markets and drive the growth of the industry.
III. Development Status of China's Solid-State Battery Industry
A. Policy Support
The Chinese government has recognized the strategic importance of solid-state batteries and has provided strong policy support for their development. This includes financial incentives, research grants, and favorable policies for companies engaged in solid-state battery research and production. For example, the government has launched initiatives to support the establishment of research and development centers for solid-state batteries and has provided subsidies for companies that invest in solid-state battery technology. These policies have created a favorable environment for the growth of the solid-state battery industry in China.
B. Market Scale
With the booming demand for electric vehicles and energy storage systems, the market for solid-state batteries in China is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. According to market research reports, the Chinese solid-state battery market is projected to reach a significant size in the next few years, driven by factors such as increasing government support, technological advancements, and growing consumer demand for electric vehicles.
C. Technology Research and Development
China has made significant progress in solid-state battery technology research and development. Many universities, research institutions, and companies are actively engaged in research on solid-state batteries, covering areas such as materials development, battery design, and manufacturing processes. Some of the leading research institutions in China have achieved breakthroughs in areas such as high-performance solid electrolytes and advanced battery architectures. Moreover, Chinese companies are also collaborating with international partners to accelerate the development and commercialization of solid-state batteries.
IV. Analysis of China's Solid-State Battery Leading Enterprises
A. Qingtao Energy
Company Background and History
Qingtao Energy was founded by a team led by academician Nan Cewen of Tsinghua University. The company has its roots in the State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics and Fine Processing at Tsinghua University. Since its establishment, Qingtao Energy has been dedicated to the research and development of solid-state lithium batteries and has made significant progress in building an integrated industrial chain.
Technological Innovations
a. Phased Development Strategy
Qingtao Energy has adopted a phased strategy for the development of solid-state batteries. The first-generation product combines oxides and polymers, while the second generation integrates oxides, halides, and polymers. This approach allows the company to gradually improve the performance and stability of its batteries while minimizing technical risks.
b. Research and Development Team
The company has a strong research and development team composed of experts and scholars from Tsinghua University and other leading institutions. This team has extensive experience in the field of materials science and battery technology and is constantly exploring new materials and technologies to improve the performance of solid-state batteries.
Industrial Layout
a. Production Bases
Qingtao Energy has established production bases in multiple locations, including Kunshan, Jiangsu; Inner Mongolia; Chengdu Pidu; Yichun, Jiangxi; and Taizhou, Zhejiang. These bases are equipped with advanced production facilities and technologies to ensure high-quality production of solid-state batteries.
b. Supply Chain Partnerships
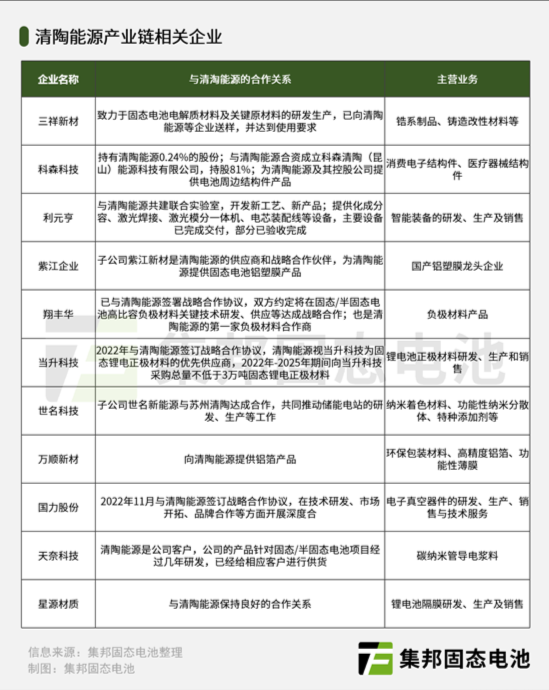
The company has formed strategic partnerships with a number of suppliers to ensure a stable supply of raw materials and components. For example, Sanxiang New Materials supplies solid-state electrolyte materials, Xiangfenghua is a negative electrode material cooperator, and Easpring is the supplier of positive electrode materials. These partnerships help Qingtao Energy to optimize its supply chain and reduce production costs.
Customer Collaborations
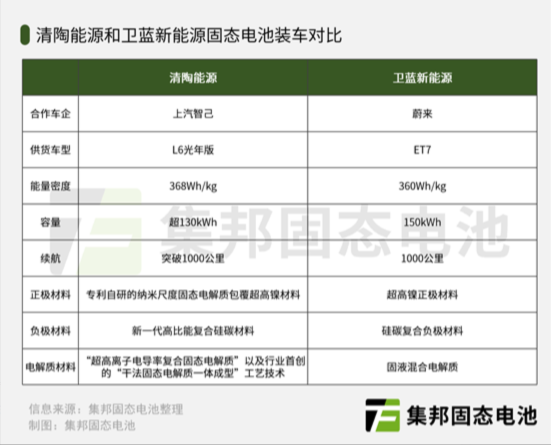
Qingtao Energy has established cooperation relationships with several major automakers, including SAIC, BAIC, and GAC. The company's solid-state batteries have been tested and validated by these automakers, and some models are expected to be equipped with Qingtao Energy's batteries in the near future. In particular, the cooperation with SAIC has been very close, with SAIC becoming the largest investor in Qingtao Energy through multiple rounds of fund participation.
B. Weilan New Energy
Company Background and History
Weilan New Energy is the industrialization platform for solid-state battery technology of the Clean Energy Laboratory of the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Initiated by renowned experts such as Chen Liquan, known as "the first person in China's lithium battery industry," the company has a strong scientific research background and is committed to the research and development and production of all-solid-state lithium batteries.
Technological Innovations
a. In-situ Solidification Solution
Weilan New Energy has developed an in-situ solidification solution for solid-state batteries. This technology involves injecting liquid to maintain good physical contact between the electrolyte and electrode materials and then converting the liquid electrolyte into a solid electrolyte through chemical or electrochemical reactions. This approach addresses issues such as high voltage, safety, lithium dendrite formation, and volume expansion, improving the performance and safety of solid-state batteries.
b. Research and Development Team
The company has a highly qualified research and development team with expertise in materials science, electrochemistry, and battery engineering. This team is constantly working on improving the technology and performance of solid-state batteries through innovation and optimization.
Industrial Layout
a. Production Bases
Weilan New Energy has production bases in Liyang, Jiangsu; Huzhou, Zhejiang; Fangshan, Beijing; and Zibo, Shandong. These bases are designed to meet the growing demand for solid-state batteries and are equipped with advanced production technologies and quality control systems.
b. Supply Chain Partnerships
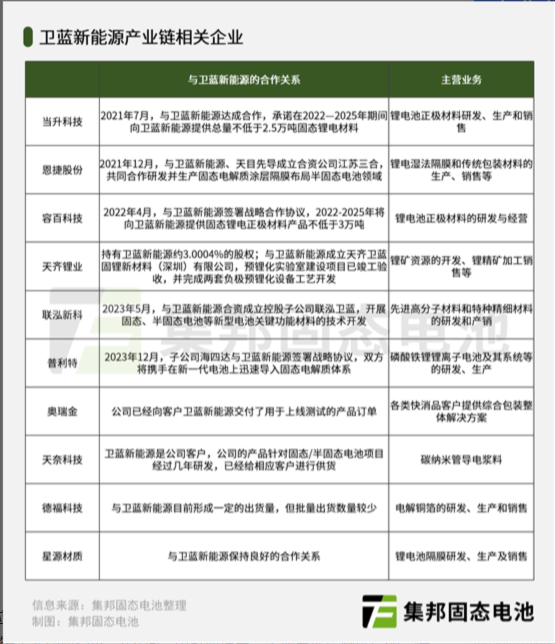
Weilan New Energy has collaborated with a number of leading suppliers in the battery industry to ensure the quality and stability of its products. For example, Easpring and Ronbay Technology supply solid-state lithium battery cathode materials, Tianqi Lithium develops anode prelithiation technology, and Enjie shares researches and develops solid-state electrolyte-coated separators. These partnerships help Weilan New Energy to build a strong supply chain and enhance its competitiveness.
Customer Collaborations
Weilan New Energy has close cooperation with new energy vehicle companies such as NIO, Geely, and Xiaomi. The company's solid-state batteries have been delivered to NIO and are being tested and evaluated by other automakers. In addition, Geely and Xiaomi have participated in the investment in Weilan New Energy through capital injection, indicating their confidence in the company's technology and future prospects.
V. Comparison between Qingtao Energy and Weilan New Energy
A. Scientific Research Background
Both Qingtao Energy and Weilan New Energy have strong scientific research backgrounds. Qingtao Energy is backed by Tsinghua University, which is renowned for its excellence in materials science and engineering. Weilan New Energy, on the other hand, is supported by the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, which has a long history of research in the field of energy and materials. These scientific research institutions provide strong technical support and talent resources for the two companies, enabling them to conduct in-depth research and development in the field of solid-state batteries.
B. Technological Routes
Qingtao Energy's Phased Strategy
Qingtao Energy's phased development strategy allows for a gradual improvement in battery performance while minimizing risks. By starting with a combination of oxides and polymers and then integrating halides in the second generation, the company is able to explore different materials and technologies to optimize the performance of its solid-state batteries. This approach also gives the company more flexibility in responding to market demands and technological challenges.
Weilan New Energy's In-situ Solidification Solution
Weilan New Energy's in-situ solidification solution is a unique approach that addresses some of the key challenges in solid-state battery technology. By converting liquid electrolytes into solid electrolytes through chemical or electrochemical reactions, the company is able to improve the safety and performance of its batteries while maintaining good physical contact between the electrolyte and electrode materials. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the manufacturing process of solid-state batteries and could lead to significant cost reductions and performance improvements.
C. Industrial Layout
Production Capacity and Locations
Both companies have established production bases in multiple locations to meet the growing demand for solid-state batteries. Qingtao Energy has bases in Kunshan, Jiangsu; Inner Mongolia; Chengdu Pidu; Yichun, Jiangxi; and Taizhou, Zhejiang. Weilan New Energy has bases in Liyang, Jiangsu; Huzhou, Zhejiang; Fangshan, Beijing; and Zibo, Shandong. The locations of these bases are strategically chosen to take advantage of local resources, markets, and government support.
Supply Chain Partnerships
Both companies have formed strategic partnerships with suppliers in the battery industry to ensure a stable supply of raw materials and components. Qingtao Energy has partnerships with Sanxiang New Materials, Xiangfenghua, Easpring, Wanshun New Materials, Zijiang Enterprise, Coscen Technology, Cnano Technology, and Sinoma. Weilan New Energy has partnerships with Easpring, Ronbay Technology, Tianqi Lithium, Enjie shares, Polyt's subsidiary Haishida, Aojin, Defu Technology, and Sinoma. These partnerships help the companies to optimize their supply chains, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
D. Customer Collaborations
Qingtao Energy and Automakers
Qingtao Energy has established cooperation relationships with several major automakers, including SAIC, BAIC, and GAC. The company's solid-state batteries have been tested and validated by these automakers, and some models are expected to be equipped with Qingtao Energy's batteries in the near future. The cooperation with SAIC is particularly close, with SAIC becoming the largest investor in Qingtao Energy through multiple rounds of fund participation.
Weilan New Energy and New Energy Vehicle Companies
Weilan New Energy has close cooperation with new energy vehicle companies such as NIO, Geely, and Xiaomi. The company's solid-state batteries have been delivered to NIO and are being tested and evaluated by other automakers. Geely and Xiaomi have also participated in the investment in Weilan New Energy through capital injection, indicating their confidence in the company's technology and future prospects.
VI. Challenges Faced by China's Solid-State Battery Industry
A. Technical Difficulties
Solid-State Ion Diffusion
One of the major technical challenges in solid-state battery technology is the issue of solid-state ion diffusion. Solid electrolytes generally have lower ionic conductivity compared to liquid electrolytes, which can lead to slower charging and discharging rates and reduced battery performance. Researchers are working on developing new materials and architectures to improve the ionic conductivity of solid-state electrolytes and overcome this challenge.
Compatibility between Electrode Materials and Solid-State Electrolytes
Another challenge is the compatibility between electrode materials and solid-state electrolytes. Different electrode materials may have different chemical and physical properties, which can affect their interaction with the solid electrolyte. This can lead to issues such as interface resistance, poor cycling performance, and reduced battery lifespan. Finding suitable electrode materials and optimizing the interface between the electrode and the electrolyte is crucial for improving the performance and stability of solid-state batteries.
Manufacturing Process Complexity
The manufacturing process of solid-state batteries is relatively complex compared to traditional batteries. This is due to the need for precise control of materials and processes to ensure the quality and performance of the batteries. For example, the preparation of solid electrolytes often requires high-temperature sintering or other complex processes, which can increase production costs and reduce production efficiency. Developing more efficient and scalable manufacturing processes is essential for the commercialization of solid-state batteries.
B. Cost Issues
The high cost of solid-state batteries is a major obstacle to their widespread adoption. This is mainly due to the expensive materials and complex manufacturing processes involved. For example, some of the key materials used in solid-state batteries, such as solid electrolytes and advanced electrode materials, are currently very expensive. In addition, the manufacturing process of solid-state batteries requires specialized equipment and technologies, which also contribute to the high cost. Reducing the cost of solid-state batteries through technological innovation and economies of scale is crucial for their market penetration.
C. International Competition Pressure
The global solid-state battery market is highly competitive, with companies from Japan, South Korea, the United States, and other countries also vying for leadership. Japanese automakers such as Toyota, Honda, and Nissan are actively researching and developing all-solid-state batteries and have made significant progress in this field. South Korean companies like LG New Energy, Sk On, and Samsung SDI are also investing heavily in solid-state battery technology. In the United States, there are many start-up battery companies that are backed by strong academic, corporate, and capital support. China's solid-state battery industry faces intense competition from these international players and needs to continuously improve its technology and competitiveness to maintain its leading position in the global market.
VII. Conclusion
China's solid-state battery industry is at a critical stage of development, with both opportunities and challenges. The leading enterprises such as Qingtao Energy and Weilan New Energy are making significant contributions to the development of the industry through technological innovation and industrial layout. However, the industry also faces technical difficulties, cost issues, and international competition pressure. To achieve sustainable development, China's solid-state battery industry needs to continue to strengthen policy support, promote technological innovation, reduce costs, and strengthen collaborative innovation. With the joint efforts of all parties, China's solid-state battery industry is expected to achieve greater success in the future and play an important role in promoting the global transition to sustainable energy and transportation.






