Lithium battery cathode materials are pivotal constituents influencing the performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of lithium-ion batteries. An in-depth understanding of these materials is indispensable for optimizing battery technology across various industries. Let's embark on a comprehensive journey into the realm of lithium battery cathode materials to uncover their significance, diverse types, synthesis methodologies, and potential applications.
A plethora of cathode materials contribute to the functionality and efficacy of lithium-ion batteries. These materials encompass lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, lithium manganese oxide, and ternary materials like nickel cobalt manganese oxide (NCM) and lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (NCA). Each material boasts distinct properties, providing unique advantages and applications in battery technology.
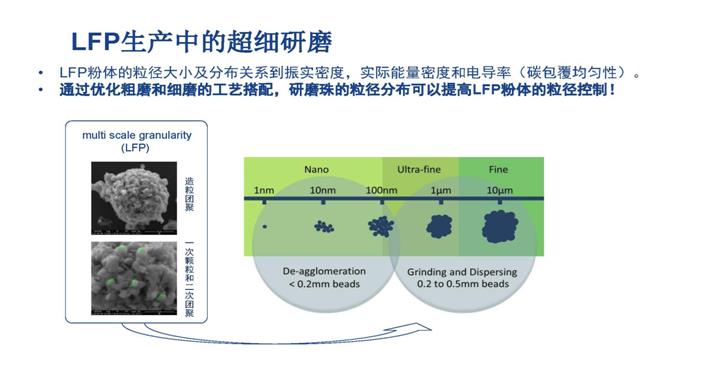
Among the array of cathode materials, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4 or LFP) emerges as a standout choice due to its remarkable density, performance, and cost-effectiveness. With a theoretical specific capacity of 170mAh/g and an actual specific capacity exceeding 150mAh/g, LiFePO4 exhibits exceptional potential across various applications. Its prolonged lifespan and outstanding performance position it prominently, particularly in the electric vehicle industry, where durability and efficiency are paramount.
In the synthesis of lithium iron phosphate, solid-phase synthesis stands as a widely employed and matured approach. This method, often employing carbon thermal reduction, entails meticulous control and processing of raw materials. Iron sources such as ferrous oxalate, iron oxide, and iron phosphate, alongside lithium sources like lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide, are meticulously mixed in accordance with stoichiometric ratios. Phosphorus sources including ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and diammonium phosphate further contribute to the synthesis process.
Researchers persistently strive to augment the synthesis efficiency of LiFePO4 through innovative methodologies. Modifications to the preparation process, encompassing optimized heating profiles and raw material compositions, have yielded significant enhancements in material properties and battery performance. These advancements underscore the continuous pursuit of refining lithium battery technology to meet evolving demands.
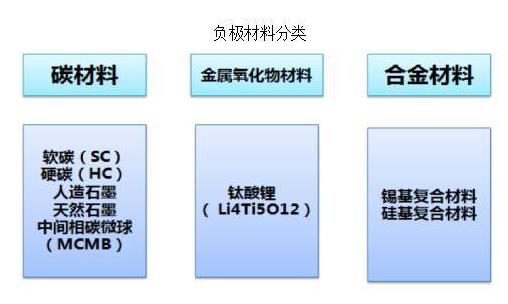
Comprehensive battery optimization necessitates an understanding of not only cathode materials but also negative electrode materials. Primary categories of negative electrode materials encompass carbon materials, metal oxide materials, and alloy materials. While graphite presently dominates the landscape, the exploration of alternative materials such as graphene, lithium titanate, and silicon-carbon composites harbors promising potential for future advancements.
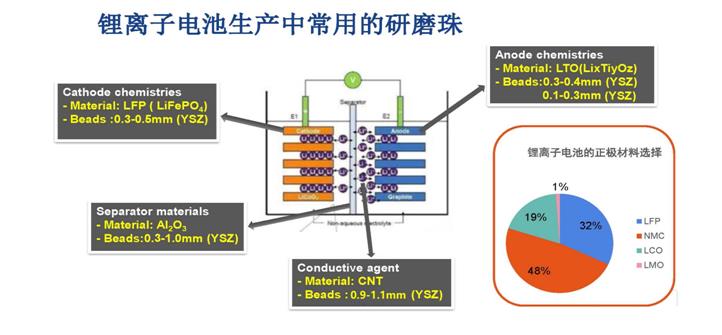
In the quest for refining negative electrode materials, precise grinding techniques play a pivotal role in achieving desired particle sizes and distributions. Zirconium oxide beads, varying in sizes from 0.1mm to 0.3mm, are extensively utilized in the grinding process for silicon-carbon negative electrode materials. These techniques facilitate the production of fine particles, thereby enabling improved battery performance and efficiency.
The realm of lithium battery cathode materials is brimming with innovation and potential. As researchers and industries continue to push the boundaries of battery technology, the exploration and optimization of cathode and negative electrode materials remain paramount. Through collaborative efforts and advancements in synthesis methodologies, the journey towards more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable lithium-ion batteries is well underway.

Submit your demand,
we will contact you ASAP.

Sanxin New Materials Co., Ltd. focus on producing and selling ceramic beads and parts such as grinding media, blasting beads, bearing ball, structure part, ceramic wear-resistant liners, Nanoparticles Nano Powder

