The electric vehicle (EV) industry has witnessed explosive growth in recent years, driven by the global push towards sustainable transportation. This growth has spurred an intense demand for higher - performance batteries. Solid - state electrolytes have emerged as a revolutionary solution to meet these demands, as they offer significant advantages over traditional battery materials. These materials are key to enhancing battery performance, safety, and energy density. However, the production of solid - state electrolytes is a complex and challenging process that requires precise control and advanced manufacturing equipment.

In the production of solid - state electrolytes, especially those based on oxides such as the highly promising garnet - type electrolytes, extremely fine powder grinding is essential. The quality of the powder directly impacts the performance of the solid - state electrolyte and, consequently, the overall performance of the battery. Traditional ball mills have proven to be inadequate in meeting the stringent requirements of this production process. The unique properties and complex chemistries of solid - state electrolyte materials demand more sophisticated milling techniques.
In the solid - state reaction process, which is crucial for large - scale production of pre - sintered powders, sand mills play an indispensable role. By utilizing yttria - stabilized zirconia beads, sand mills can effectively grind pre - sintered powders to the submicron level. This level of grinding is of utmost importance as it significantly enhances the sintering activity of the powders. Improved sintering activity not only leads to better quality solid - state electrolytes but also supports the subsequent production steps in battery manufacturing. In China's solid - state battery technology development, which primarily follows the oxide route, sand mills have become an essential part of the production process. Whether in semi - solid or fully solid - state battery production, solid - state electrolytes are the cornerstone. Hence, the significance of sand mills in preparing solid electrolytes cannot be overstated, and future research and development efforts are expected to focus on optimizing their use for this key material.
The sand mill, also known as a bead mill, is a wet ultrafine grinding machine that has evolved from the traditional ball mill. In the past, high - end sand mill markets were dominated by foreign companies such as NETZSCH and BUHLER. However, the situation has changed significantly, and now China has over 200 domestic sand mill manufacturers. This growth in the domestic industry has led to a shift in the market share, with international companies losing ground, especially in applications where material stability requirements are not extremely high.
Sand mills are generally categorized into two main types based on the arrangement of the grinding chamber: vertical and horizontal. Each type has its own unique working principle, advantages, and limitations.
The operation of a vertical sand mill involves several key steps. First, a feed pump is used to transport materials from the bottom upwards into the grinding chamber. Under the combined action of pressure and centrifugal force, the materials create a vertical circulation within the chamber. This circulation pattern is crucial for the grinding process as it allows the slurry to be continuously processed.
During this circulation, the slurry experiences intense mechanical actions between the grinding beads. These actions include emulsification, dispersion, kneading, and grinding. Through these processes, the materials are rapidly ground to the desired fineness. One of the significant advantages of the vertical sand mill is its ability to separate the material from the grinding beads using a liquid level difference. This separation mechanism effectively solves the problem of clogging that is often encountered in other grinding systems. By preventing clogging, the vertical sand mill can operate continuously, ensuring a stable and efficient grinding process.
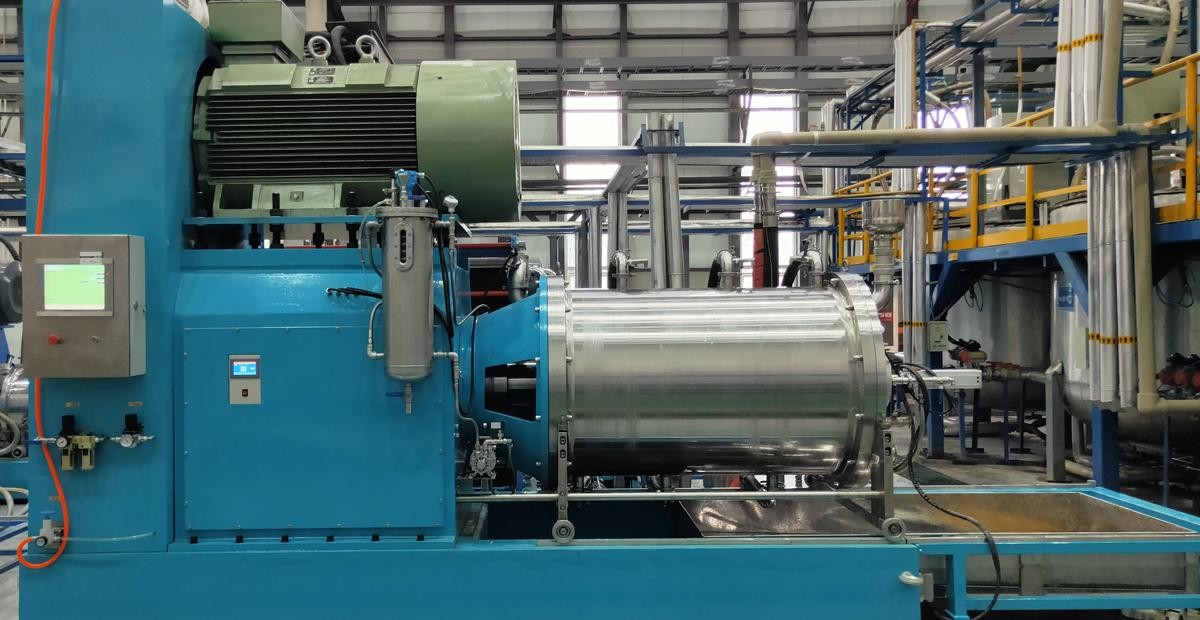
In a horizontal sand mill, the process begins with a pump feeding pre - dispersed and wetted solid - liquid mixtures into the grinding chamber. Inside the chamber, high - speed rotating dispersers play a vital role. These dispersers agitate the material and the grinding media simultaneously. The intense agitation generates strong collisions and shear forces within the mixture.
These mechanical forces act on the particles in the material, reducing their size and breaking up any aggregates. This results in the production of finely ground material. To separate the ground material from the grinding media, a dynamic separator is employed. The separated material then exits the chamber through an outlet pipe, completing the grinding process.
1. Sealing
Vertical sand mills generally do not require mechanical seals. This is a significant advantage as mechanical seals can be a source of maintenance issues and additional costs. In contrast, horizontal sand mills require mechanical seals. The presence of these seals not only increases the complexity of the equipment but also leads to higher maintenance requirements and associated costs over the life of the machine.
2. Cost
While the initial price difference between vertical and horizontal sand mills may not be substantial, the long - term cost implications are different. Due to the need for mechanical seal maintenance in horizontal sand mills, their overall maintenance costs are higher. This makes vertical sand mills a more cost - effective option in certain applications, especially when considering the total cost of ownership over an extended period.
3. Applicability
Horizontal sand mills are well - suited for large - scale production scenarios. Their design allows for higher throughput and efficient grinding of large volumes of materials. They are also capable of handling fine material grinding with good precision. On the other hand, vertical sand mills, with their unique screenless design, have the advantage of avoiding clogging issues. This enables them to produce finer and more efficient materials. However, their output may be relatively lower compared to horizontal sand mills. Therefore, the choice between vertical and horizontal sand mills depends on the specific requirements of the production process, including factors such as production scale, material fineness requirements, and budget constraints.
As the demand for solid - state batteries in the EV industry continues to grow, there will be a continuous drive to improve sand mill technology. Future advancements may focus on several aspects. One area of interest is improving the efficiency of the grinding process to further reduce particle size and increase the uniformity of the ground powder. This could involve the development of new grinding media or optimization of the grinding chamber design.
Another potential direction is enhancing the reliability and durability of sand mills. By reducing maintenance requirements and increasing the lifespan of the equipment, manufacturers can improve the overall productivity and cost - effectiveness of solid - state electrolyte production. Additionally, there may be efforts to integrate sand mills with other production processes in a more seamless manner, enabling better control and optimization of the entire solid - state electrolyte manufacturing chain.
In conclusion, sand mills have emerged as a critical component in the production of solid - state electrolytes for the electric vehicle industry. Their unique working principles and capabilities make them well - suited for the fine grinding requirements of these advanced materials. As the industry evolves, continued innovation in sand mill technology will be essential to meet the growing demands for high - quality solid - state electrolytes and to drive the development of more efficient and reliable electric vehicle batteries.
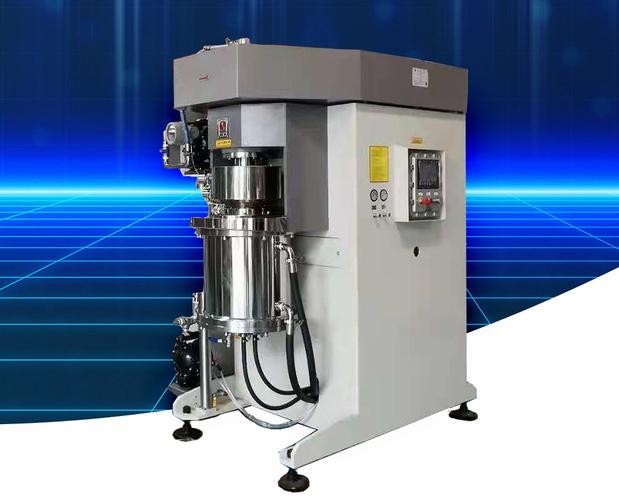

Apart from solid - state electrolyte production for electric vehicles, sand mills also find applications in other industries that require fine grinding of materials. In the paint and coating industry, sand mills are used to grind pigments and additives to achieve the desired color intensity, gloss, and stability. The ability to produce fine and uniform particles ensures better dispersion in the paint formulation, resulting in high - quality coatings with improved performance.
In the pharmaceutical industry, sand mills play a crucial role in the production of drug formulations. They are used to grind active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients to the required particle size. This is important for controlling the dissolution rate, bioavailability, and overall efficacy of the drugs. The precise grinding achieved by sand mills helps in meeting the strict quality standards of the pharmaceutical sector.
In the ceramic industry, sand mills are employed to grind ceramic powders. This enables the production of ceramics with improved density, strength, and surface finish. The fine grinding of ceramic materials helps in reducing defects during the sintering process and results in high - quality ceramic products.
In the operation of sand mills, environmental and energy considerations are becoming increasingly important. The use of efficient grinding media and optimized grinding processes can reduce energy consumption. For example, the development of lighter and more durable grinding beads can reduce the energy required to drive the rotation of the grinding chamber. Additionally, proper maintenance and operation of sand mills can prevent leaks and spills of materials and grinding media, minimizing environmental pollution.
In terms of waste management, the design of sand mills can be improved to facilitate the recovery and reuse of grinding media. This not only reduces waste but also lowers the overall cost of production. Furthermore, the selection of materials for sand mills and their components can be made with environmental sustainability in mind, choosing materials that are recyclable and have a lower environmental impact.
The research and development of sand mill technology are ongoing to address the challenges and opportunities in various industries. In academia and research institutions, there are studies focused on understanding the fundamental physics of the grinding process in sand mills. This includes research on the interaction between grinding media, materials, and the grinding chamber under different operating conditions. By gaining a deeper understanding of these processes, researchers can develop more accurate models for predicting and optimizing the performance of sand mills.
In the industry, companies are investing in the development of new sand mill designs. This includes the exploration of innovative grinding chamber geometries, improved separation systems, and advanced control mechanisms. For example, the development of intelligent control systems that can adjust the operation of sand mills in real - time based on the properties of the materials being ground can significantly improve the quality and efficiency of the grinding process.
Moreover, collaborations between different stakeholders, such as equipment manufacturers, material suppliers, and end - users, are becoming more common. These collaborations aim to accelerate the development and adoption of new sand mill technologies by sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise. Through these combined efforts, the future of sand mill technology looks promising, with the potential to revolutionize the way fine grinding is carried out in various industries.

Submit your demand,
we will contact you ASAP.

Sanxin New Materials Co., Ltd. focus on producing and selling ceramic beads and parts such as grinding media, blasting beads, bearing ball, structure part, ceramic wear-resistant liners, Nanoparticles Nano Powder

