In an era where technology advances at a breakneck pace, a groundbreaking development has emerged from the State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices at South China University of Technology. Led by the distinguished Professor Xia Zhiguo, the research team has made a significant leap forward in lighting technology with the introduction of a new near-infrared fluorescent transparent ceramic composed of MgO:Cr3+. This innovation, detailed in a recently published paper, highlights the creation of a blue-light laser-driven near-infrared light source device capable of delivering an unprecedented output power of 6W. Such a remarkable achievement opens a myriad of possibilities in applications ranging from long-distance night vision to non-destructive testing imaging, setting a new standard in the field.
The evolution of Blue Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) has heralded the fourth generation of semiconductor lighting, pushing the envelope for light source devices' performance and application. In response to the growing demands for more sophisticated lighting solutions, the industry has seen a pivotal shift towards the integration of blue laser diodes (LDs) with fluorescent conversion materials. This innovative approach, unlike traditional LED-based solutions, leverages the intense brightness of blue LDs to activate fluorescent conversion materials, paving the way for a new era of laser fluorescent light sources. The potential applications for this technology are vast and varied, including aviation and maritime illumination, underwater lighting, laser fluorescent display projectors, and high-power near-infrared light source devices, to name a few.
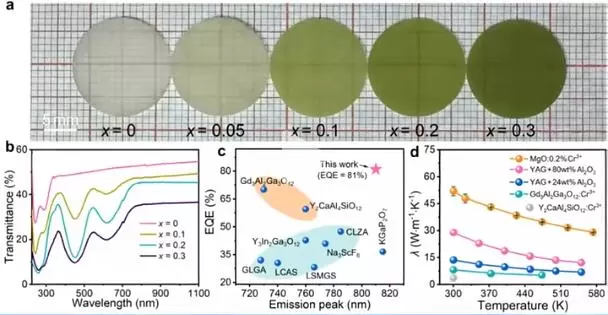
The centerpiece of this technological breakthrough is the high-stability MgO:Cr3+ fluorescent transparent ceramic, which boasts a near-perfect performance. With a broad band near-infrared emission peak at 810nm, this material has set a new record for external quantum efficiency at 81%. Such efficiency is not just a numerical achievement; it represents a significant leap forward in the development of high-power, laser-driven near-infrared light sources.
By employing this cutting-edge ceramic technology, the team successfully developed a prototype device capable of penetrating 3cm thick opaque materials to achieve high-resolution imaging. This breakthrough demonstrates the technology's immense potential in enhancing night vision capabilities, revolutionizing industrial flaw detection, and advancing non-destructive testing imaging for medical instruments.

The success of this research is not solely the achievement of the researchers involved but also a testament to the collaborative environment within the School of Materials Science and Engineering/Luminescent Materials and Devices National Key Laboratory at South China University of Technology. Doctoral student Liu Gaochao, under the guidance of Professor Xia Zhiguo, played a pivotal role in this project, highlighting the importance of nurturing young talent in advancing scientific research. Furthermore, the project received substantial support from esteemed institutions, including the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program, and the Guangdong Pearl River Talent Program.
As we look towards the future, the implications of this research are far-reaching. With its unparalleled efficiency and broad application spectrum, the new near-infrared light source device promises to revolutionize the way we perceive and utilize light. From enhancing night vision capabilities to improving non-destructive testing methods, the potential of this technology is only beginning to be unlocked.
Sanxin New Materials Co., Ltd., a company specializing in ceramic milling balls, nanoparticles and nanopowders, wear-resistant ceramics, and abrasion-resistant ceramics.
Article source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-024-01400-7#change-history

Submit your demand,
we will contact you ASAP.

Sanxin New Materials Co., Ltd. focus on producing and selling ceramic beads and parts such as grinding media, blasting beads, bearing ball, structure part, ceramic wear-resistant liners, Nanoparticles Nano Powder

